Moreover, the rising popularity of medical aesthetics among men as societal norms shift has led companies to target them more directly, though women are expected to continue to make up the vast majority of the consumer base (c.90%-95% through 2030).
Overall, the penetration1 of the aesthetics treatment market is very low — for example, c.3% in the injectables market. However, c.18% of current non-users of injectables would consider purchasing treatments in the future, implying a much larger addressable population of c.6x-7x current market size, or $70 billion-$80 billion. Manufacturers have increased their marketing spend in an effort to realize sales to these potential customers.
The medical aesthetics market is also attracting new customers seeking wellness-oriented treatments (e.g., intravenous and injection therapies). This innovative approach, blending health benefits with cosmetic enhancement, has the potential to contribute significantly to market growth by appealing to health-conscious consumers seeking comprehensive wellness and beauty regimens.
Trend 2: Innovative products are expanding treatment options to broaden the consumer base
The market for medical aesthetics treatments has experienced significant growth, offering nonsurgical alternatives to invasive procedures. These treatments, which include both pharmaceuticals and energy-based devices, have expanded consumer choices and increased adoption rates. They cover a wide range of applications, allowing for the targeted treatment of specific aesthetic concerns.
One notable development in the industry is the creation of longer-lasting neurotoxin injections and premixed injectables. These advancements streamline the treatment process and enhance consumer throughput. Additionally, innovative materials like silk protein injections in a hyaluronic acid matrix are leading the way in faster tissue regeneration.
Skin boosters such as Profhilo and fat-targeting treatments such as Kybella are also making strides. Profhilo offers deep hydration, while Kybella focuses on removing fat from targeted areas, e.g., under the chin. These innovations are designed to cater to diverse skin types, treatment needs and demographic groups, widening the consumer base.
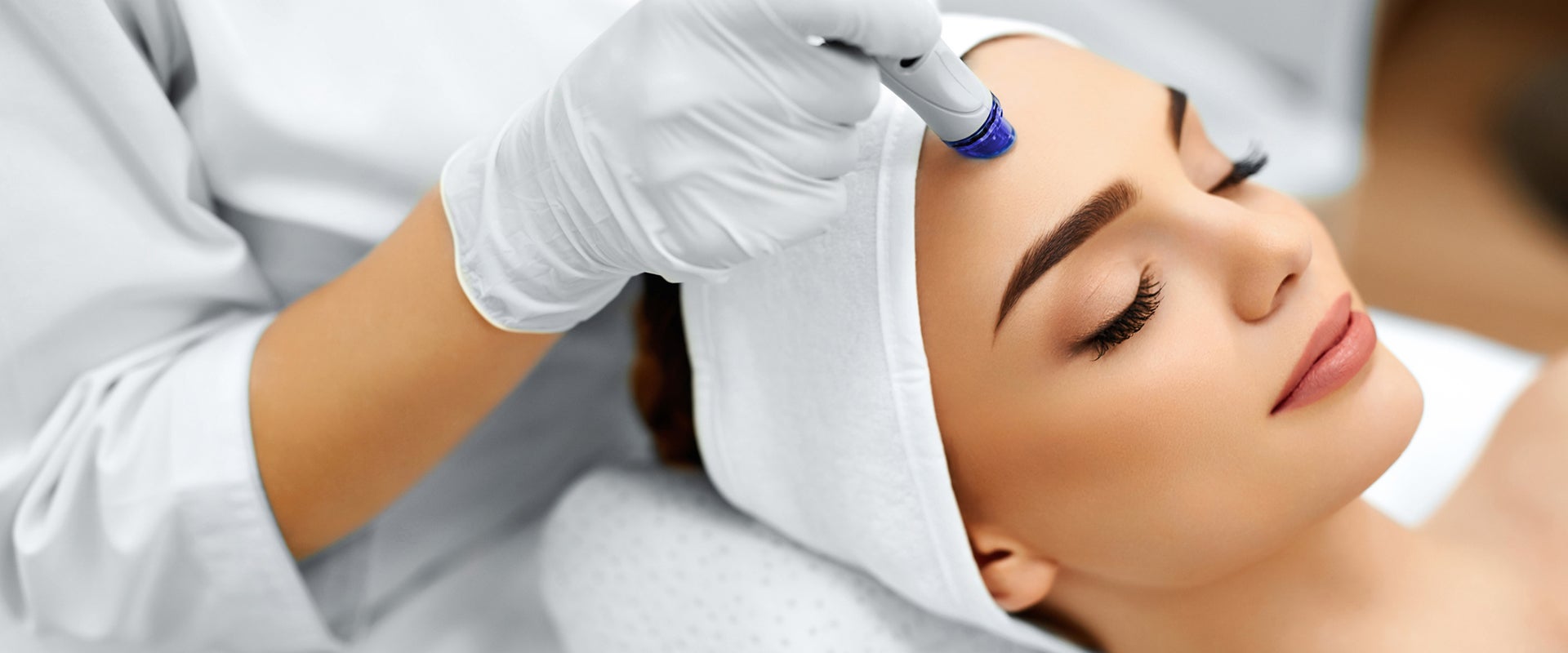
Select brands such as Hydrafacial and CoolSculpting have also cultivated significant customer pull through innovative solutions and treatment experience to capture consumer interest and generate demand. Additionally, both of these brands actively market to end consumers, creating pull for channel participants to adopt these treatments.
Furthermore, the industry’s innovation extends to off-label use of drugs for nonsurgical treatments. An example is Ozempic, an anti-diabetic drug being used as a weight-loss solution. This reflects the industry’s adaptability and innovative mindset. However, it underscores the necessity for clear regulatory and ethical oversight. Practices offering aesthetics treatments must ensure credibility and manage consumer expectations carefully, including informing consumers of potential side effects.
In response to diverse consumer demands, manufacturers are diversifying their portfolios with a range of new products and services, tapping into both established and emerging consumer needs. This strategic expansion allows for more targeted upselling and cross-selling opportunities, as businesses can offer tailored solutions across different demographics and aesthetic preferences, such as age-specific treatments or enhancements popularized through social media or cultural trends. On the device side, best-in-class technologies are attracting more consumers by improving treatment outcomes, e.g., enhanced efficacy, faster recovery. Laser technologies for skin resurfacing, tattoo removal and hair removal continue to evolve, while new treatments such as radiofrequency microneedling are gaining traction among consumers. Technological advancements are also enabling average treatment volumes per clinic to grow by reducing procedure durations and improving ease of use. Notably, players such as Matex Lab market combinations of pharmaceuticals and devices to advance synergistic treatment approaches, such as its pegylated dermal filler alongside the Sectum radiofrequency handheld device for volume enhancement and skin regeneration.
Trend 3: Med spas and aesthetics clinics are rising to meet this demand and expand consumer access
Med spas sit at the intersection of medical aesthetics treatments and broader beauty treatments and are an increasingly popular option for consumers. In the U.S. in 2023, c.40%-45% of medical aesthetics treatments were performed in med spas/aesthetics clinics; in the U.K. and Ireland, this figure was c.50%-55%.
Med spas are increasingly becoming the preferred venue for consumers seeking injectable treatments, surpassing dermatology and cosmetic surgery practices This trend is driven by the exceptional consumer experience offered by med spas, positioning them for significant growth within the medical aesthetics market. Notably, the expansion of players such as Thérapie and Laser Clinics in the U.K. via greenfield locations and Cosmetique Totale in Europe via a combination of M&A and greenfield has rapidly increased the availability of aesthetics treatments. This has led to supply-driven growth as consumers are increasingly exposed to med spa treatments, prompting consumer interest and exploration of services.
The med spa market is poised for continued growth, even amid economic downturns. Despite a decrease in consumer spending, the number of med spas and the rate of penetration are expected to rise. One key aspect of this market is strong customer loyalty. About 70% of med spa customers express interest in memberships, which have been shown to boost both spending per visit and visit frequency. However, only one-third of med spas offer such memberships currently, highlighting a significant opportunity area.
This preference is financially beneficial for med spas, as members tend to spend about 44% more than nonmembers do. Furthermore, after just three visits, around 76% of consumers view themselves as “lifetime” customers of a med spa. This sense of loyalty further manifests through referrals, with consumers reporting they have referred others to med spas an average of three times over the past year.
Med spas have become a preferred workplace for nurses, especially those seeking relief from the stress and burnout experienced during COVID-19. This challenging period led many nurses to reconsider their careers in traditional healthcare settings, such as hospitals. Additionally, some healthcare providers currently in these conventional roles, who do not yet offer aesthetics treatments, have shown a keen interest in doing so within the relaxed environment of a med spa. This interest suggests that med spas could become a key employer in the future.
However, administering injectables, the most popular service offered by med spas, requires specialized skills. Being a nurse does not automatically qualify someone to perform these treatments. This highlights the essential role of master injectors, who have received advanced training in these specific procedures, and underscores the need for targeted training and development programs to fulfill the sector’s specific needs effectively.
Med spa professionals prioritize both work experience and financial factors when selecting their work environment. Key aspects such as work-life balance, in-house training, career progression, development opportunities and quality of management are particularly valued. These work experience factors tend to outweigh financial considerations for most. Med spas stand out in this respect, offering superior work experiences compared to other settings.
This alignment with these professionals’ preferences allows med spas, especially those operating on a larger scale, to more effectively attract talent. They leverage competitive compensation, a positive workplace culture, and structured training and development programs. Such programs are crucial for equipping these professionals with the skills needed for specialized treatments like injectables, which are highly sought after and also generate higher profit margins.
In the U.S., med spas are experiencing rapid growth compared to other settings, attributed to consumer perceptions of a better environment, superior customer service, access to a broader range of treatments and lower costs. The sector is anticipated to expand at approximately 10%-12% per year between 2022 and 2027. Injectables, making up the largest service segment by value (about 40%-50%), are expected to grow even faster, at around 12%-14% annually (see Figure 2). In the U.K., med spas/aesthetics clinics are expected to grow between 10% and 11% over the same period, with injectables leading as the largest service segment in value (c.30%-40%).