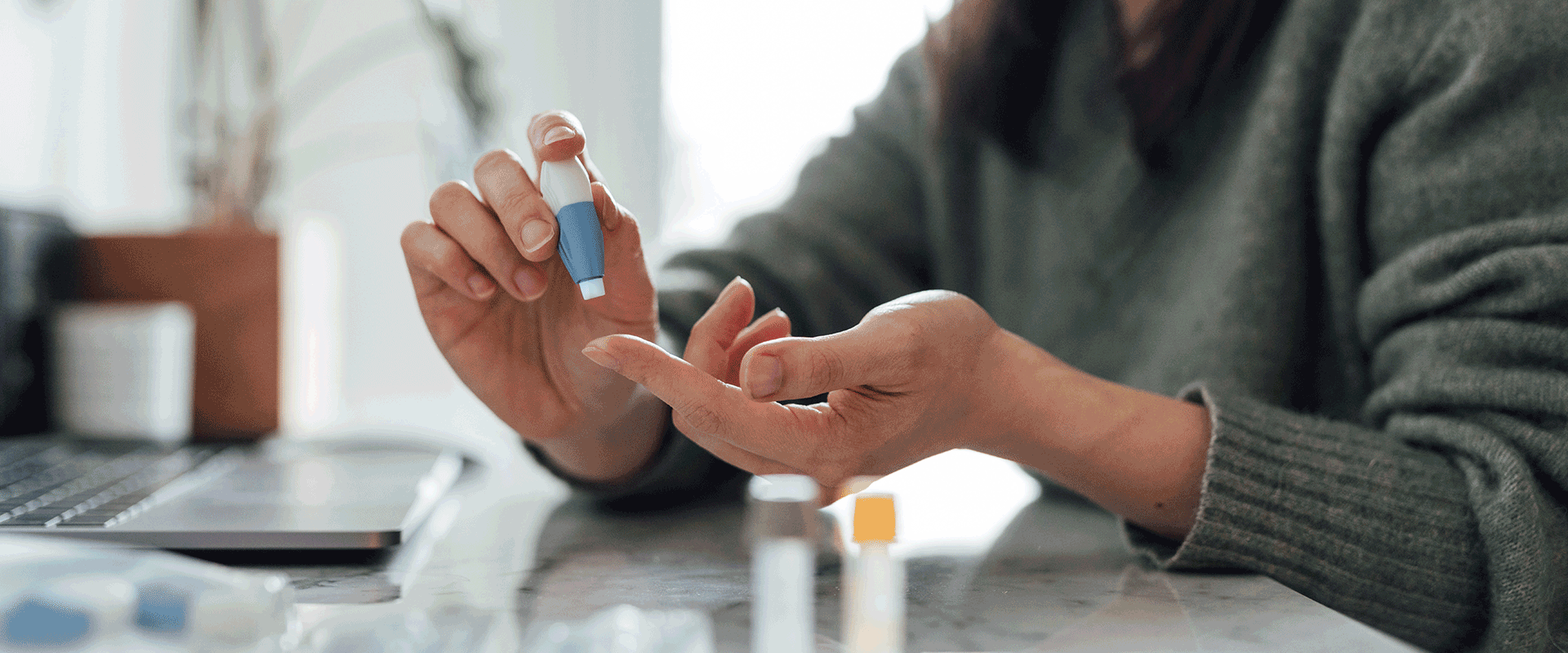
Capturing value in home healthcare
For companies and investors looking to benefit from the growth trajectory of home-health-in-a-box products, there are likely to be significant and varied opportunities to gain a piece of the action. Existing stakeholders, including home healthcare product companies, packaging converters, contract packagers and contract manufacturers, can build on their success by focusing on several important themes and market needs. Healthcare product companies operating in the clinical setting should consider adjacencies that will allow them to benefit from the home health market tailwinds.
Products that we expect to win in the marketplace are those that best meet the needs of patients, which will in turn feed into new product design requirements. These include such features as:
- Ease of use and deliverability (e.g., easy-open, intuitive design)
- Miniaturization (e.g., smaller component parts)
- Increased connectivity (e.g., providing patient monitoring and test results to patients and healthcare providers)
- Increased measuring capabilities and accuracy
- Real-time analysis of data
- Limited, easy maintenance (e.g., safe and effective storage and cleaning)
As more patients have their healthcare product needs fulfilled through direct-to-patient shipping, shipping safety and packaging become important focus areas. Packaging must be robust enough to protect products during last-mile shipping to the home and safe enough for use (e.g., sterile barrier packaging), but at the same time companies are under pressure to reduce packaging’s plastic content and replace it with more ecologically friendly materials. Safe and environmentally responsible product disposal and recyclability will also be important differentiators, as the patient bears responsibility for disposal in the home health setting (versus the healthcare provider in a traditional healthcare setting). Packaging converters that are well aligned to these unique at-home healthcare product and packaging needs and have the requisite capabilities (e.g., customer codesign resources to design for ease of use, access to recycled materials, high-resolution printing suitable for self-administration instructions, proprietary molds/die-cutting equipment for high-value conversion, sterilization-compatible coatings) are expected to be significantly competitively advantaged.
Ongoing innovation in consumer-centric medical-grade products will call for new component development, customized packaging designs, and cutting-edge supply chain management and sourcing. Acquiring these capabilities or nurturing them internally is another way to play in the promising home-health-in-a-box market.